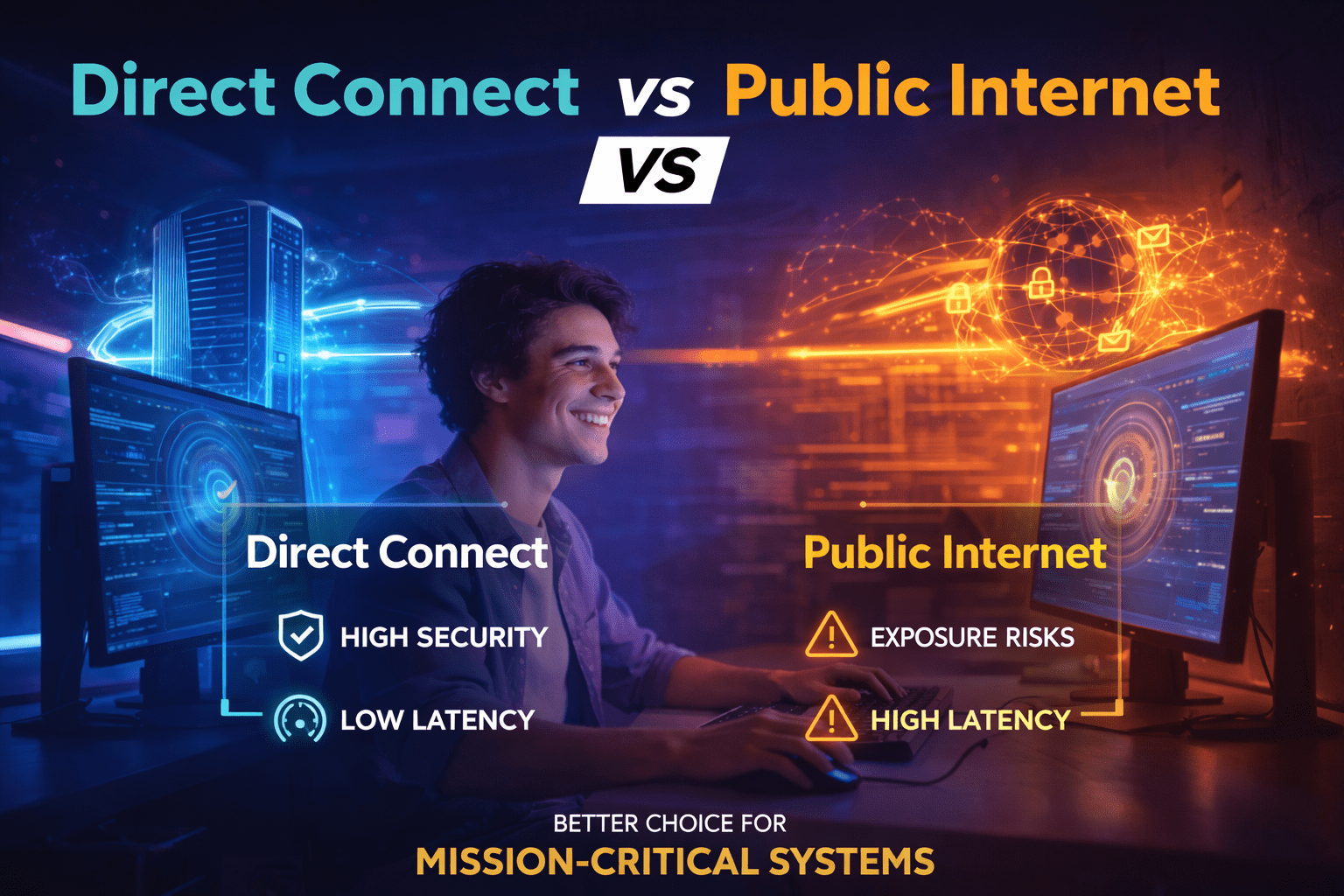
Choosing between Direct Connect vs Public Internet is an important decision for modern businesses. Both provide connectivity. However, they work in very different ways. In simple terms, Direct Connect is private. Public Internet is shared. Because of this, speed, security, and stability are different. So, which one should your company choose? Let’s break it down clearly. What Is Direct Connect? Direct Connect is a private network connection. It links your office or data center directly to a cloud provider. Unlike Public Internet, traffic does not pass through shared networks. Therefore, performance stays consistent. As a result, latency becomes predictable. In addition, data transfer is more secure. Many enterprises use Direct Connect for: Because the connection is dedicated, congestion has minimal impact. Businesses often combine this with Cloud Connect solutions to improve multi-cloud performance. What Is Public Internet? Public Internet is the shared global network most companies use daily. It routes traffic through many public systems. Therefore, setup is simple and cost-effective. However, performance may change depending on traffic conditions. During peak hours, latency can increase. In some cases, packet loss may occur. As a result, business applications may slow down. For browsing and email, Public Internet works well. However, for mission-critical workloads, it may not be sufficient. Direct Connect vs Public Internet: Performance Comparison When comparing Direct Connect vs Public Internet, performance is the most visible difference. Direct Connect provides stable speed and consistent latency. Because traffic flows through private routes, congestion is reduced. On the other hand, Public Internet depends on ISP routing paths. Therefore, performance can vary throughout the day. If your business relies on real-time applications, stable connectivity is essential. Direct Connect vs Public Internet: Security Differences Security is another major factor in the Direct Connect vs Public Internet comparison. Direct Connect uses private infrastructure. Therefore, exposure risk is significantly lower. Public Internet requires additional protection such as VPN or encryption. Although these tools improve safety, traffic still travels through shared networks. As a result, Direct Connect provides better control for sensitive business data. If your organization uses Internet Exchange services for optimized peering, integration with Direct Connect can further enhance routing efficiency. Direct Connect vs Public Internet: Cost Comparison Cost is often the first concern when evaluating Direct Connect vs Public Internet. Public Internet has lower initial cost. Setup is also faster. However, Direct Connect can reduce long-term operational risk. Because performance is stable, downtime becomes less likely. In addition, predictable bandwidth supports business continuity. Therefore, the real question is not only price. It is long-term business impact. Direct Connect vs Public Internet: Which One Scales Better? Scalability is critical for growing companies. Public Internet works well for small workloads. However, bandwidth limitations appear as traffic increases. Direct Connect supports higher capacity and stable throughput. As a result, it is better suited for expanding enterprises. If your company plans digital transformation, scalability should be part of your decision. Conclusion: Direct Connect vs Public Internet The choice between Direct Connect vs Public Internet depends on your business priorities. Public Internet is flexible and affordable. However, Direct Connect offers stronger performance, better security, and improved scalability. Evaluate your infrastructure carefully. The right connectivity strategy supports long-term growth.