
In the vast digital landscape, seamless connectivity is essential for businesses and individuals alike. At the heart of this connectivity lies a fundamental concept known as IP transit. But what exactly is IP transit, and how does it work?
What is IP Transit?
IP transit, also known as internet transit, is a commercial service that enables data to travel to its intended destination by traversing multiple networks. Essentially, it allows Internet traffic to move from one network to another, ensuring seamless connectivity and communication.
How Does IP Transit Work?
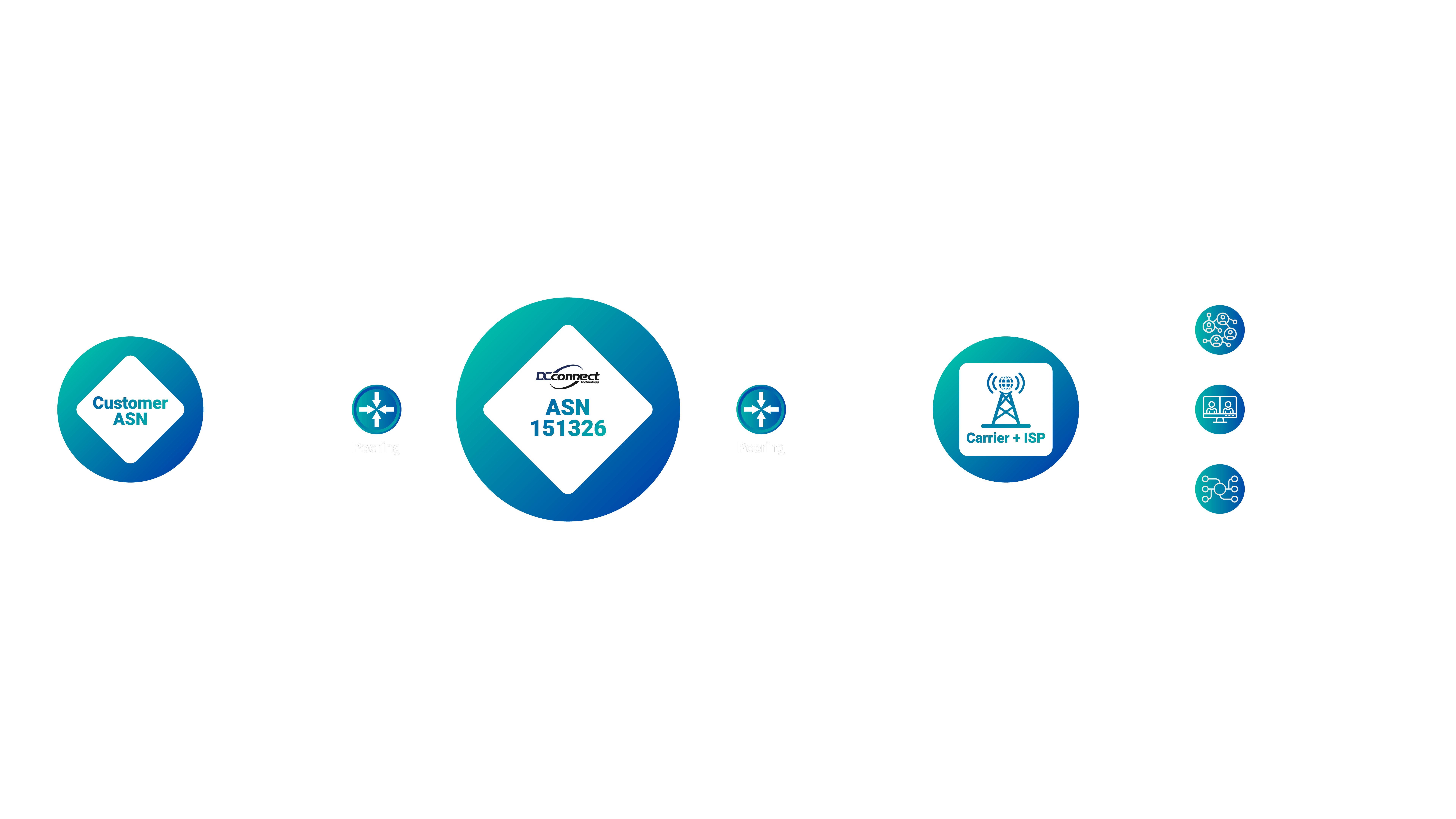
IP transit works at the level of backbone networks using a protocol called Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). The internet is a global network of interconnected public networks known as autonomous systems (AS), which use BGP to direct traffic between them. Each AS is assigned a unique Autonomous System Number (ASN) to identify them on the network and blocks of IP addresses to identify their network devices.
When a customer connects to an IP transit provider’s network using BGP, they pay a transit fee to access the provider’s network, opening up high-capacity access to the whole internet.
Benefits of IP Transit
IP transit is integral to the global network infrastructure, bridging the gap between internal, private networks and the vast public Internet. By providing full access to the Internet, IP transit ensures that businesses, service providers, and end-users can connect and communicate without barriers, maintaining the efficiency and reliability of Internet connectivity.
Understanding how IP transit works is crucial for businesses that rely on robust and reliable internet connectivity. By leveraging IP transit, organizations can ensure seamless data flow across the internet, enhancing their operational efficiency and global reach.



